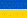
Practical training of residents is achieved through the systematic and active participation of young doctors in diagnostic and therapeutic work, clinical rounds, other types of practical activities in anesthesiology and intensive care.
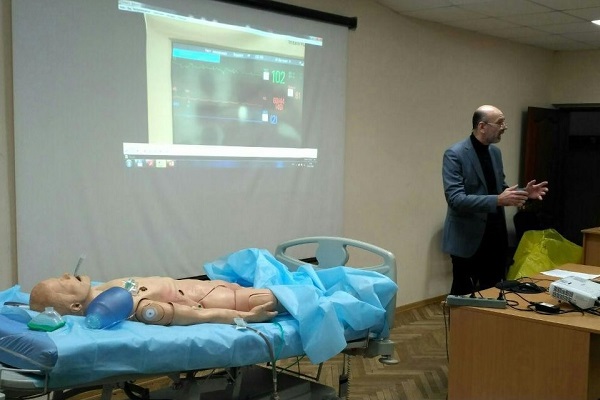
Modern conditions of training specialists dictate the need for a more profound approach to their practical training. This is particularly the case with decision making and immediate practical actions of the physician when dealing with patients in critical condition. However, the training of specialists on this issue is limited by many factors, in particular the impossibility of practical illustration of the diversity of clinical situations, moral and ethical and legislative constraints.
In their studies, Seymour S. et al. clearly demonstrated the practical and educational value of simulational modelling for surgical specialties, demonstrating that simulation training methods shorten the time of surgeons' work when performing laparoscopic cholecystectomy by 29% and reduce the number of errors by 85%.
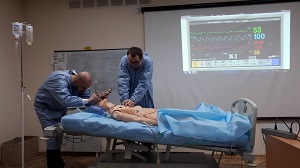
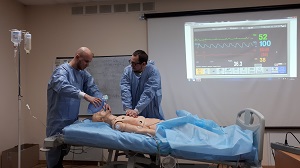
These training methods should occupy a significant place in the training of future anesthesiologists.
Proceeding from this, at the Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care of Shupyk National Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, on January 11, 2019, another simulation study was conducted on an important clinical problem "Massive Bleeding in Surgery". The lesson was preceded by a lecture on this problem, which was read by the head of the department of anesthesiology and intensive care, Professor Loskutov OA.

The technical aspects of prevention, diagnosis and emergency treatment on mannequins with full clinical simulation were demonstrated.
As residents noted, attending such classes helps to consolidate practical skills and prepares for making the right decisions in extreme clinical situations, when the decision and implementation of time manipulation is limited and largely determines the speed and quality of the anesthetist's actions.